What Is Profitability Analysis? A Complete Guide to Measuring Profit Margins

What Is Profitability Analysis? A Complete Guide to Measuring Profit Margins
Understanding where to invest and how specific variables contribute to your total profits is essential for improving your company’s financial health.
Profitability analysis delivers the insights you need to make smart, strategic decisions that generate more return from your investments—but you need the right approach and accurate data to get meaningful results.
This guide covers the need-to-knows of profitability analysis: what it means, why it’s important, and how to avoid common challenges.
Download the free ebook: Spend Analysis Toolkit
What is profitability analysis?
Profitability analysis measures the profit generated by different business activities to help you identify which ones contribute most to your bottom line.
It builds on spend analysis by breaking down both costs and revenues across specific profit drivers, such as products or services, customer groups, and sales channels, to show you the where, why, and how of your profitability.
The benefits of profitability analysis done right
Profitability analysis is a powerful tool for optimizing your financial strategy. It helps you identify which activities to prioritize and which to eliminate for maximum impact.
Profitability analysis helps you:
- Develop pricing strategies: Establish value-based pricing models that maximize profit margins through a detailed understanding of profitability.
- Optimize resource allocation: Redirect your financial and operational resources toward the most profitable activities for a higher return on investment.
- Boost operational efficiency: Identify your costliest processes to guide working capital investments in automation and workflow improvements.
- Improve strategic decision-making: Make informed decisions based on data-driven insights and more accurate financial reporting.
For example, an automotive company featured in McKinsey’s “Introducing the Next-Generation Operating Model” report discovered that design and engineering development time was a major cost driver. By focusing on this area, the company shortened its development times and improved its profit margins.
What are the key components of profitability analysis?
A successful profitability analysis requires the right inputs, calculations, and categorization.
Profitability analysis relies on three core components:
- Revenue streams: Total revenue broken down into measurable segments for a granular view of profitability
- Costs: Accurate allocation of direct costs (expenses directly tied to producing a saleable product) and indirect costs (operating expenses that support the business but aren't linked to a specific product)
- Profitability metrics: Formulas that compare revenue and expenses to determine the profitability of a specific product or activity
To ensure you’re using reliable numbers, invest in modern financial systems that automate real-time data collection and minimize the risk of human errors, such as Order.co’s intelligent spend management software.
4 methods of profitability analysis
You can analyze profit in several ways, from simple company-level formulas to more complex methods that examine margins across products, market segments, and sales activities.
Four common methods include:
- Profit ratios (ratio analysis): Financial performance metrics for calculating profitability, such as margin ratios (profit from sales) and return ratios (returns to shareholders)
- Cost-volume-profit (CVP) analysis: A method used primarily for break-even analysis and understanding how changes in sales volume, pricing, and costs impact profitability
- Product/customer profitability analysis: Revenue and cost allocation for individual products, customers, or customer segments
- Activity-based costing (ABC): Precise allocation of indirect costs for specific products, customers, or sales channels
Each method helps calculate profitability, but to extract deep insights about specific profit drivers, you need a strategic approach.
Steps to conduct a profitability analysis
Missed steps and inaccurate calculations lead to costly financial planning mistakes. Here’s a simple, easy-to-follow strategy for conducting an accurate profitability analysis.
1. Define objectives and scope
Your analysis should aim to answer a specific question. For example, “Which product line was the most profitable in Q3?”
Getting specific about your objective creates a clear path to valuable profit insights.
Once you’ve defined your question, clearly specify what you intend to measure (e.g., a customer segment, sales channel, or specific SKU). Then set a timeframe and assign responsibilities to the relevant team members to prevent scope creep.
2. Collect relevant revenue and direct costs data
Data fuels your analysis and is critical for ensuring accurate results that support smart financial decisions.
First, create a data checklist. Identify every source needed to calculate profitability, including:
- Sales data: Pull detailed revenue data from your finance systems for the entity you're analyzing.
- Direct costs data: Extract cost of goods sold (COGS) data from inventory or manufacturing systems and your accounts payable ledger, covering anything directly tied to producing or delivering goods or services.
- Administrative costs data: Gather Information on staff salaries, administrative processes, and customer support, which often represent indirect costs but may be partially direct in detailed analyses.
- Customer data: Extract sales activity and customer interaction details from your CRM systems.
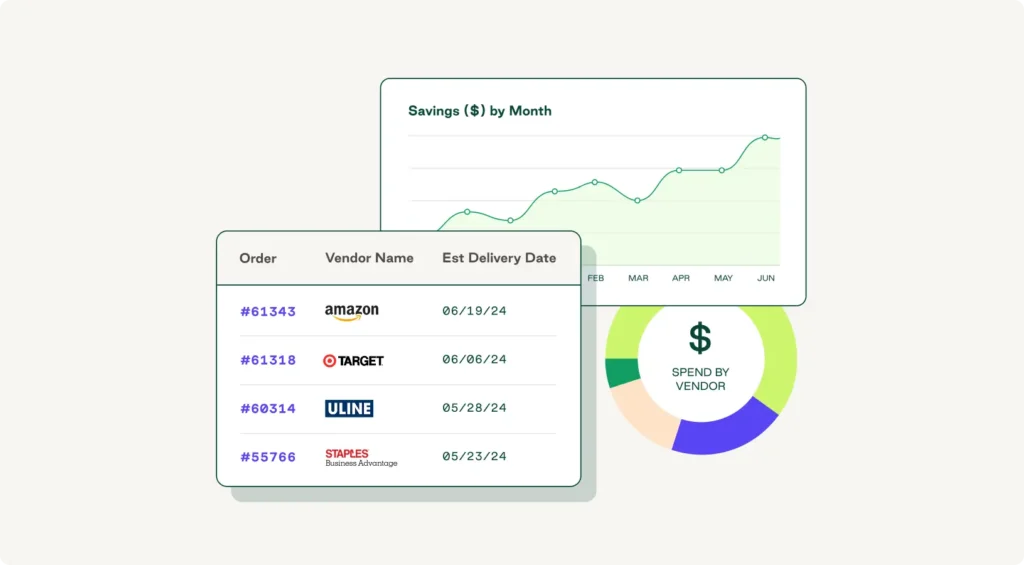
- Procurement data: Collect purchasing records from your procurement software systems, including tail spend on supplies, outside services, and software subscriptions that affect cost allocation.
To guarantee accuracy and consistency, establish standard naming conventions, rules for handling missing data, and one system as your single source of truth for resolving discrepancies.
3. Track and allocate indirect costs
Indirect cost allocation carries the greatest risk in profitability analysis. Incorrectly assigning costs leads to flawed calculations that can skew your decision-making.
A systematic approach helps reduce risk:
- Divide your indirect costs: Split your operating costs into categories, such as overhead, travel and events, marketing and advertising, supplies, and software.
- Create cost pools: Group similar costs within each indirect spend category. For example, break overhead into warehousing, administration, and customer support.
- Establish cost drivers: Identify the activity that causes each cost pool to increase. For example, the driver for warehousing costs might be cubic feet of storage space per product or order volume shipped per customer.
- Calculate your activity rate: Divide the total cost of each pool by the total volume of its cost driver.
Procurement analysis software is a lifesaver when it comes to accurate cost allocation. The technology automatically centralizes your cost data and tracks spending across vendors, product types, and locations.
For example, if customer support costs $10,000 and the support team handled 1,000 tickets, your activity rate is:
Total Cost of Customer Support / Total Number of Support Tickets = Activity Rate
$10,000 / 1,000 = $10
To measure a specific customer's profitability, you'd multiply the number of support tickets by the activity rate. If they raised 50 tickets, their total activity cost for support tickets would be $500 (50 × $10).
4. Calculate profitability
Now comes the most important part. Calculating your profitability quantifies the performance of your object of analysis and answers the original question you set out to explore.
Create a flexible model that allows you to test multiple variables, such as “How does a 12% increase in material costs affect the profitability of this specific product line?”
You can do this using Excel spreadsheets, business intelligence (BI) tools, or financial planning software. Or, you can use our free variance report template to save time.
To calculate different aspects of profitability, use these financial ratios:
- Gross profit margin %: ((Revenue – COGS) / Revenue) × 100
- Net profit margin %: (Net Profit / Revenue) × 100
- Operating profit margin %: (Operating Profit / Revenue) × 100
- Contribution margin $: Revenue – Variable Costs
To find your break-even point, perform a cost-volume-profit (CVP) analysis by dividing total fixed costs by contribution margin per unit.
Be sure to document all cost allocations and profit calculations, and validate your results by comparing them to past performance or expected benchmarks.
How profitability analysis informs strategic decisions
Understanding profitability isn’t just about checking balance sheets and calculating profit ratios—you need to compare your results with industry standards and past performance to see the complete picture.
Establish profitability benchmarks by researching average profit margins for similar businesses or products. You can source this information from industry reports and financial data providers by searching “[industry/product] profit margin benchmarks.”
Here are a few resources to help you out:
- Industry Benchmarks of Gross, Net, and Operating Profit Margins
- US Profit Margins by Sector
- US Profit Margin Industry Averages
Comparing your results with industry standards helps highlight areas for improvement. Are you spending more on materials than your competitors? Are manual processes driving up your costs where automation could help?
Once you’ve drawn your conclusions, use your findings to improve financial forecasting, prioritize profitable activities, and support better future profitability. You can also download our free financial projections template to get a jump start on your financial planning initiatives.
Fitting profitability analysis into your business plans
| Strategic area | How profitability analysis helps |
| Product portfolio management | Identifies your most profitable product mix to inform R&D investment and phase out underperformers |
| Pricing optimization | Helps you set tiered prices based on the cost-to-serve for specific customer segments |
| Customer segmentation | Pinpoints your most profitable customers and customer groups for sales and marketing purposes |
| Operational efficiency | Uncovers process inefficiencies and high-cost activities for spend reduction and workflow automation |
| Resource allocation | Helps you allocate purchasing budgets and resources to maximize profitability and improve cash flow |
Challenges and common pitfalls associated with profitability analysis
With so many variables at play, profitability analysis can easily go off track. Here are some of the biggest challenges to watch out for and how to avoid them.
Data quality and accessibility
Poor data quality undermines analysis. Siloed data sources, inconsistent formatting or naming conventions, and missing details are often to blame.
The solution lies in your technology and processes. Establish a single source of truth—such as an ERP system or procurement analytics tools—to act as your main data hub.
Before beginning an analysis, set clear data governance rules that dictate how you collect, label, and maintain data across all your systems.
Accurate cost allocation
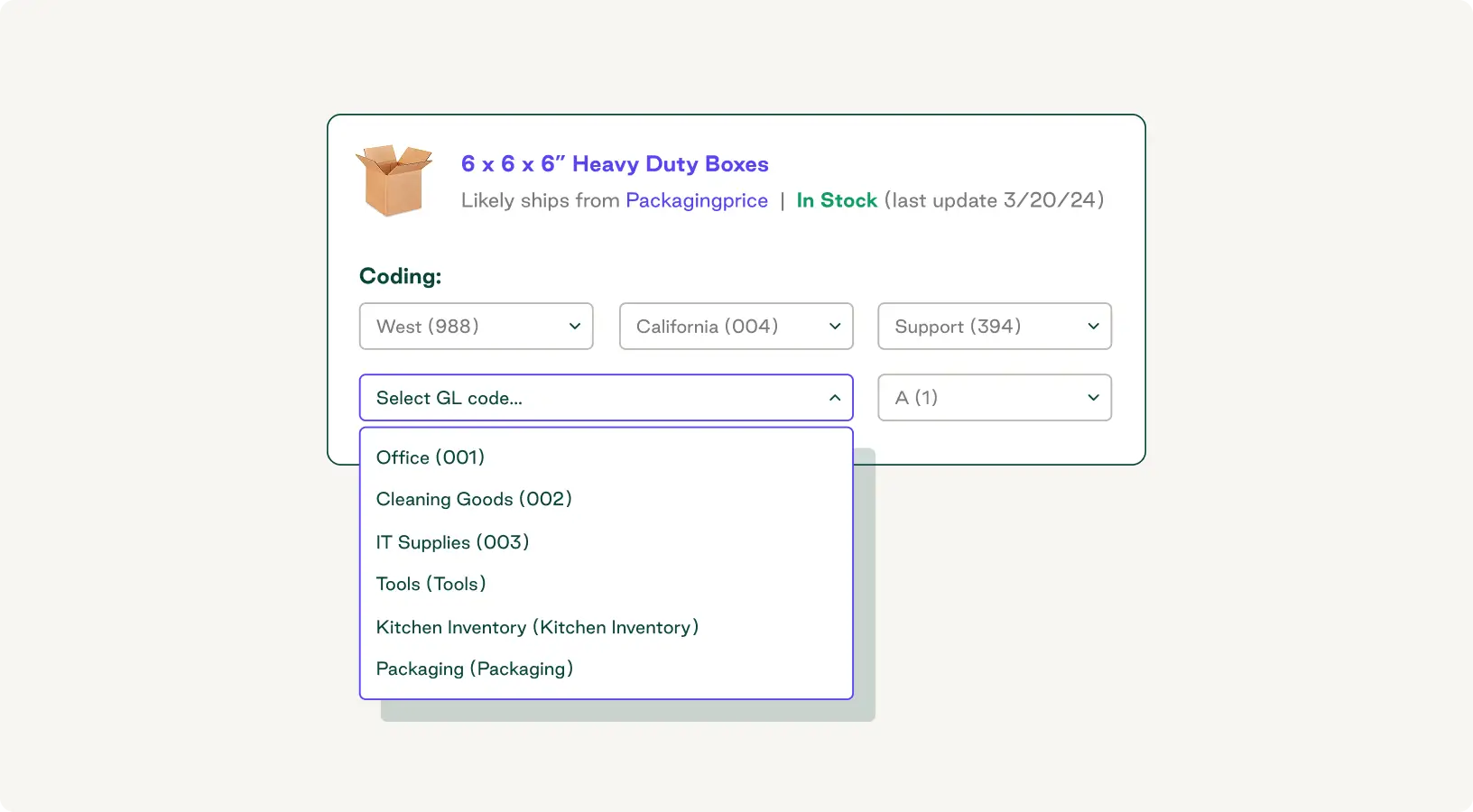
Misallocating indirect costs—such as rent, salaries, and software licenses—can distort your analysis and lead to poor financial decisions.
If costs are assigned based on rough estimates or simplified financial metrics like sales revenue, high-volume products may appear less profitable than they are, while complex, resource-heavy offerings may be under-accounted for.
Adopt a precise cost allocation method, such as activity-based costing, to ensure you’re assigning all costs based on actual consumption. Procurement software like Order.co can automatically code expenses to the correct activity and reduce manual errors.
Unclear analysis segmentation
Overly broad segments lead to generic profit metrics and missed insights. When you lump dissimilar groups together to find an average, you mask meaningful differences that drive strategic action.
To avoid flawed, one-size-fits-all results, start with a specific question and hypothesis tied to your business goals. Then, break down your profit by as many relevant variables as possible to build a clearer picture of how different profit margins affect your financial position.
How to identify and prioritize profitability levers
Manual cost tracking and spreadsheet updating can eat up countless hours of your team's time and leave room for costly errors. But accurately assigning expenses and analyzing profit drivers takes more than labor and due diligence. It requires the right tools.
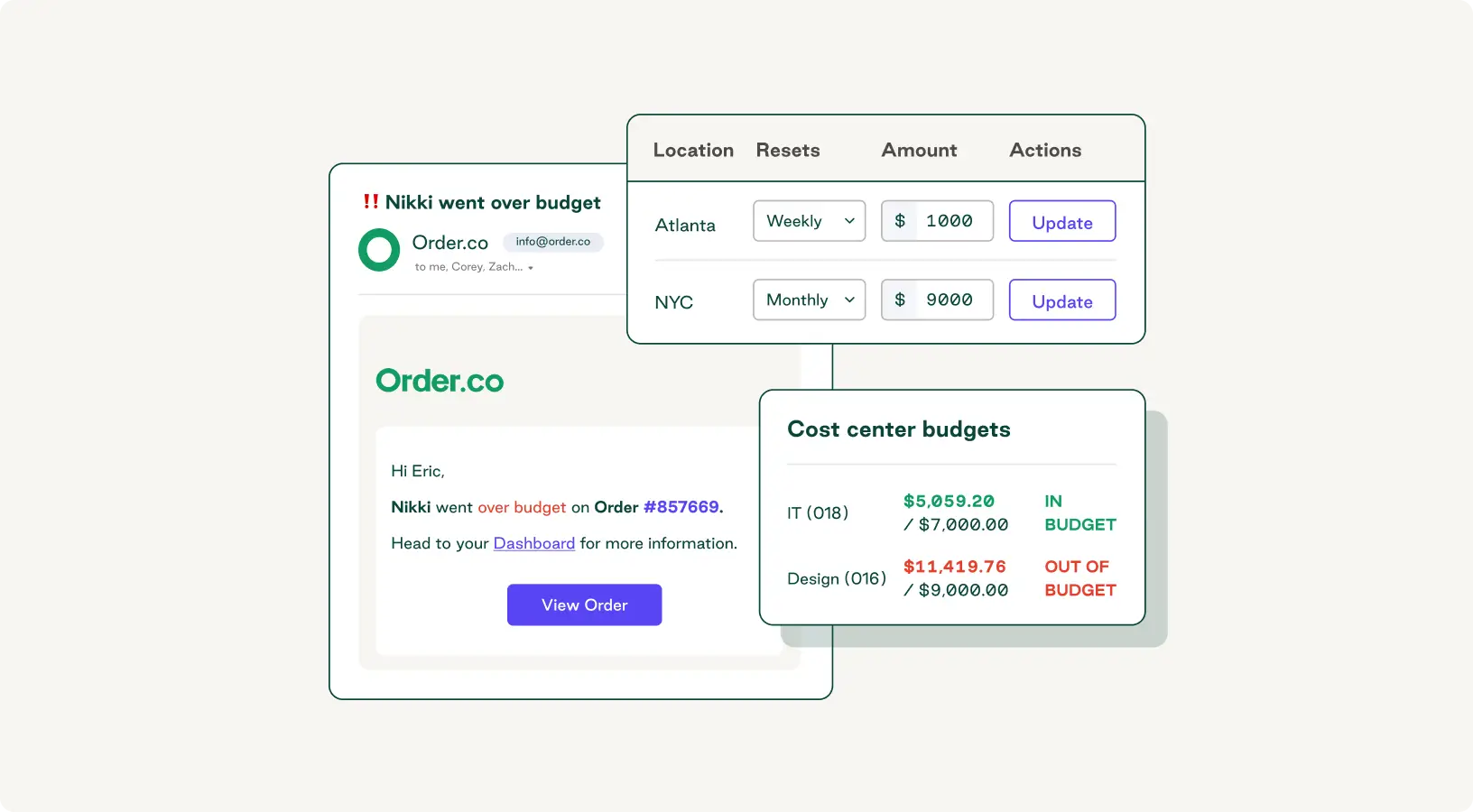
Order.co’s intelligent spend management platform helps procurement teams improve overall profitability by maximizing cost efficiency. It automates tedious tasks like breaking down transactions and assigning costs to specific items, helping eliminate manual errors and inconsistencies.
With Order.co, you can automatically track and allocate your costs, view spend performance in real time with live dashboards, and create custom budgets that drive more value from every dollar.
Schedule a free demo today to see how Order.co’s features can help you increase profitability and take control of your spend.
Get started
Schedule a demo to see how Order.co can simplify buying for your business
"*" indicates required fields



